Income tax is a tax that is paid by individuals and businesses in South Africa. Tax is compulsory for individuals and there are different levels of tax depending on your income. There are also different types of income that are taxable in South Africa.
There are three main types of income in South Africa: earned income, unearned income, and capital gains. Earned income is any income that you earn from working. This includes your salary, wages, tips, commissions, and other forms of income. Unearned income is any income that you don’t earn through work. This includes income from investments, such as dividends, interest, and rental income. Capital gains is any increase in the value of your assets, such as stocks, bonds, and property. This includes the value of items you’ve sold, such as a car, and the value of items you’ve inherited, such as property.
Income tax is paid on your earned income, unearned income, and capital gains. You pay tax on the amount of your income that is over the relevant income tax threshold. The relevant income tax threshold is different for each person, depending on your income and the amount of your income tax liabilities. The relevant income tax threshold for an
Contents
- 1 Who Must Pay Income Tax In South Africa
- 2 Types of Income Tax – Overview of income tax rates, types of income and deductions
- 3 Who Must Pay Income Tax – Who is required to pay income tax in South Africa, including individuals, companies and trusts
- 4 Requirements and Deadlines – Overview of filing requirements, deadlines and payment options
- 5 Conclusion
Who Must Pay Income Tax In South Africa
In South Africa, anyone who earns an income from a salary, business or other form of trading must pay income tax. This includes those employed in the public sector, those working for private companies, as well as those who are self-employed or run a business. All these individuals must submit a tax return each year and pay their taxes as required by law. The South African Revenue Service (SARS) is responsible for collecting these taxes and ensuring compliance with the country’s tax laws. Furthermore, non-residents of South Africa who receive income from South African sources are also liable to pay income tax in South Africa. Tax payers are entitled to certain deductions and allowances to reduce their overall tax burden, such as medical aid contributions and pension deductions.
Types of Income Tax – Overview of income tax rates, types of income and deductions
In South Africa, income tax is a legal obligation for any individual or business that earns an income. As a taxpayer, it’s your responsibility to ensure that you pay the correct amount of income tax to the South African Revenue Service (SARS). There are several types of income tax, each with their own rules and regulations, and understanding them is essential in ensuring that you comply with the law.
Income Tax Types
The two main types of income tax in South Africa are Provisional Tax and Normal Tax.
Provisional Tax
Provisional tax is a payment that is made in two instalments throughout the year, generally based on the estimated income of the taxpayer. The first instalment is due on the last day of August, and the second instalment is due on the last day of February. Provisional tax is applicable to self-employed individuals and those who have a business or rental income.
Normal Tax
Normal tax is the tax that is paid by all employees in South Africa. It is deducted from their monthly salary and is paid directly to SARS. The amount of tax that is deducted depends on the tax bracket that the individual is in.
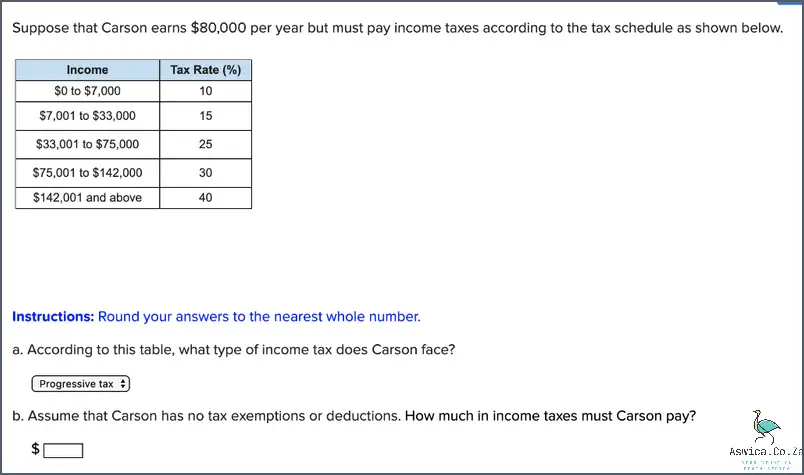
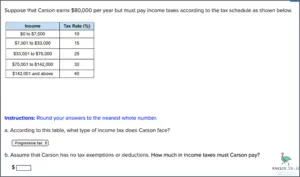
Overview of Income Tax Rates
The income tax rates for different tax brackets in South Africa are as follows:
• 0 – R50 000 – 18%
• R50 001 – R75 000 – 26%
• R75 001 – R99 000 – 31%
• R99 001 – R150 000 – 36%
• R150 001 and over – 39%
Types of Income
The types of income that are subject to income tax in South Africa are:
• Salary and wages
• Rental income
• Business income
• Interest income
• Dividend income
• Capital gains
Deductions
There are several deductions that are available to taxpayers in South Africa in order to reduce the amount of tax they are liable to pay. These deductions include:
• Medical expenses
• Retirement annuity contributions
• Donations to approved charities
• Home office expenses
• Travel expenses
• Clothing expenses
• Education expenses
It is important to remember that these deductions are only available to taxpayers who can prove that the expense has been incurred.
In conclusion, understanding the various types of income tax, the income tax rates, types of income and deductions available in South Africa is essential in ensuring that you comply with the law. It is also important to remember that these deductions are only available to taxpayers who can prove that the expense has been incurred.
Who Must Pay Income Tax – Who is required to pay income tax in South Africa, including individuals, companies and trusts
In South Africa, income tax is a form of taxation imposed by the South African Revenue Service (SARS) on individuals and companies. All South African taxpayers are required to pay income tax on their income, which includes both earned income (such as salaries, wages, and commissions) and unearned income (such as dividends, interest, and rental income). The amount of income tax an individual or company is required to pay is determined by the amount of taxable income earned in the previous financial year.

Individuals are required to pay income tax on their gross income, which includes salaries and wages, investment income, and profits from self-employment. The amount of income tax payable is based on a progressive rate structure, meaning that the more one earns, the higher percentage of tax they will pay. Individuals may also be eligible for certain deductions and tax credits, which can reduce their tax liability.
Companies, on the other hand, are required to pay income tax on their net income, which includes all income minus allowable deductions and expenses. Companies may also be eligible for certain deductions and tax credits, which can reduce their income tax liability.
Trusts are also required to pay income tax on their income, which includes profits from investments and other activities. The amount of income tax payable is based on a progressive rate structure, and trusts may also be eligible for certain deductions and tax credits.
In addition to income tax, individuals, companies and trusts may be required to pay other taxes such as capital gains tax and value-added tax. It is important to understand one’s tax obligations so that they can make sure they are in compliance with the law and are paying the correct amount of taxes.
Requirements and Deadlines – Overview of filing requirements, deadlines and payment options
When it comes to filing taxes in South Africa, understanding the requirements and deadlines can be overwhelming. For this reason, it’s important to have a comprehensive overview of the filing requirements, deadlines, and payment options available to you.
In South Africa, all individuals who have a taxable income of more than R79,000 must pay income tax. This includes individuals who are employed, self-employed, or those who receive a taxable income from investments, rental income, or other sources. The tax year in South Africa runs from 1 March to 28 February of the following year.
The first step in filing your taxes is to register with the South African Revenue Service (SARS). This can be done online, in person, or via telephone. After registering, you’ll need to submit your return before the 31st of August of each year. This return must include details of your income and deductions for the previous year.
Once your return has been submitted, you’ll be given a date when you must make your payment. This date is usually the 31st of October each year. Payment can be made in a variety of ways, including via direct bank transfer, internet banking, cash deposit, or debit order.
If you fail to submit your return or make your payment on time, you may be liable for penalties and interest. These penalties can range from 10% to 200% of the total tax due, depending on the severity of the offence.
If you’re unable to pay your tax on time, you may be able to enter into a payment agreement with SARS. This agreement must be approved by SARS and will include details of the amount due, the payment plan, and the interest rate applicable.
Filing taxes in South Africa can be a daunting task, but understanding the requirements and deadlines is the first step to getting it right. Knowing the payment options available to you will also help you make sure your taxes are paid on time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, everyone who earns an income in South Africa is liable to pay income tax. This includes individuals, companies, and trusts, as well as foreign entities who earn income from a source in South Africa. Generally, any income earned from a source within South Africa, including salaries, wages, bonuses, pensions, and profits from businesses and investments, must be declared and taxed. In addition, any foreign income received in South Africa is also taxable. Taxpayers are responsible for filing their annual income tax returns to SARS and for paying the tax due on their income.




