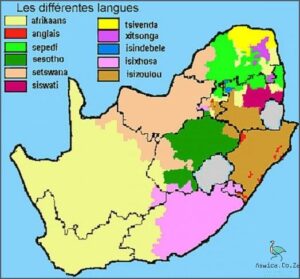
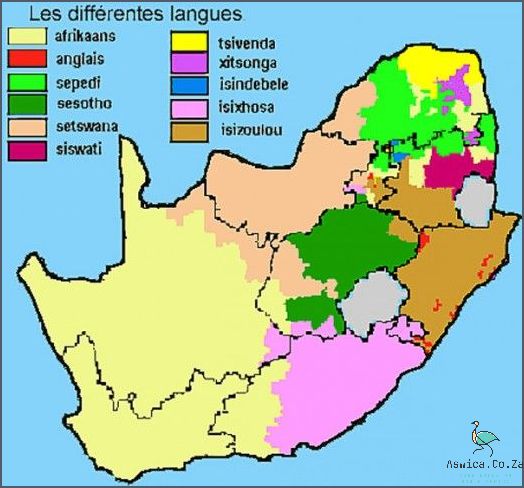
Zulu is a Southern Bantu language spoken in South Africa. It is one of the official languages of South Africa and is the first language of about 10 million people, making it the most widely spoken African language in South Africa. The majority of Zulu speakers live in the province of KwaZulu-Natal, where it is the predominant language. Other provinces where Zulu is spoken include the Eastern Cape, Gauteng, and Limpopo.
Contents
Where Is Zulu Spoken In South Africa
Zulu is a language spoken by the Zulu people of South Africa. It is the most widely spoken language in the country, with an estimated 10 million speakers. It is mainly spoken in KwaZulu-Natal Province, where the Zulu people are based, but also in some parts of Eastern Cape, Gauteng, and Mpumalanga. It is also used as a lingua franca by people of other ethnic backgrounds in the region. Zulu is one of the 11 official languages of South Africa and is widely used in media and literature. It is also used as the language of instruction in some schools.
Geographical Distribution of Zulu: Where is the language most commonly spoken?
The Zulu language is one of the most widely spoken vernaculars in South Africa, and its geographical distribution is highly varied. While the language is most commonly spoken in the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa, it can also be found throughout the rest of the country and even in neighboring countries. This article will explore the geographical distribution of the Zulu language and provide a brief overview of where it is most commonly spoken.
In South Africa, the Zulu language is most heavily concentrated in the KwaZulu-Natal province, where it is the primary language of more than 10 million people. It can also be found throughout the rest of the country, with smaller concentrations in Gauteng, the Eastern Cape, Mpumalanga, and the Western Cape. The language is also found in parts of neighboring countries such as Mozambique, Lesotho, and Swaziland.
The Zulu language has a long and storied history in South Africa, with many believing that it originated in the KwaZulu-Natal province. It is believed to have been brought to the region by Bantu-speaking migrants from Central and East Africa over a thousand years ago. The language has been strongly influenced by the languages of the Dutch and English colonists and missionaries who arrived in the region in the 18th century, as well as by Afrikaans, which is an official language in South Africa.
Within KwaZulu-Natal, the Zulu language is most commonly spoken in the rural areas of the province, with the majority of the population residing in the rural regions of KwaZulu-Natal. The language is also found in the urban centers of the province, although it is not nearly as common in these areas.
The Zulu language is also widely spoken in other African countries, particularly in Zimbabwe, Zambia, Malawi, Tanzania, and Botswana. While the language is not an official language in any of these countries, it is becoming increasingly popular in urban areas, particularly in the major cities.
In conclusion, the Zulu language is one of the most widely spoken vernaculars in South Africa and its geographical distribution is highly varied. While the language is most commonly spoken in the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa, it can also be found throughout the rest of the country and even in neighboring countries. The language has a long and storied history in South Africa, and its influence can be seen throughout the region.
History of Zulu: How did the language come to be?
The Zulu language, spoken by the Zulu people of South Africa, is one of the oldest and most widely-spoken languages on the continent. It has been spoken in South Africa for centuries, and is still spoken today by millions of people.
The Zulu people were part of the Bantu ethnic group, who migrated to South Africa from Central Africa in the 11th century. The Bantu language was the source of the Zulu language, which has its own distinct dialects and regional varieties.
The Zulu language has been used for centuries for trade, communication and cultural purposes. It was also used as the language of the royal court of the Zulu kingdom, and for religious ceremonies such as weddings and funerals. The language was also used to record the history of the Zulu people, including their wars, customs and traditions.
Today, Zulu is still spoken by millions of people in South Africa, and is the most widely-spoken language in the country. It is spoken in all of the provinces, including Gauteng, KwaZulu-Natal, Limpopo, Mpumalanga, North West and the Free State. It is also spoken in neighbouring countries such as Mozambique, Lesotho and Swaziland.
The Zulu language is a part of South African culture and history, and is an important way of connecting with the Zulu people and their history. It is also a part of everyday life in South Africa, and is spoken by people of all ages and backgrounds. It is a language that should be celebrated and preserved for future generations.
Culture and Customs: How does the language influence Zulu culture and customs?
The Zulu language is one of the most widely spoken languages in South Africa, with millions of speakers throughout the sub-Saharan region. It is a Bantu language, belonging to the Nguni group of languages. Zulu is the official language of the Zulu people, who are the largest ethnic group in South Africa, and is also widely spoken in Lesotho, Swaziland, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
The Zulu language has been heavily influenced by the culture and customs of its speakers, known as the Zulu people. This is evident in its rich vocabulary, which includes words and phrases specific to the Zulu culture and customs. For example, the Zulu people have a rich tradition of storytelling, which is reflected in their language. Zulu is filled with words and phrases used to describe various aspects of their culture, such as the traditional Zulu greeting “Sawubona”, which translates to “I see you”.
The use of proverbs is also very common in the Zulu language, and they are often used to convey deeper meanings and messages. Proverbs are a reflection of the Zulu people’s belief in the importance of wisdom and the power of words. The Zulu language also has a variety of idiomatic expressions which are used to convey feelings and emotions in a way that cannot be expressed with just words.
The Zulu language also has a strong influence on the traditional music of the Zulu people. Much of the music is sung in Zulu, and the language is used to create rich and beautiful melodies. Traditional Zulu music often includes the use of drums and other percussion instruments, and these musical instruments are also named in the Zulu language.
In addition to its influence on music, the Zulu language has also influenced many other aspects of Zulu culture and customs. For instance, it has heavily influenced the Zulu naming system, with Zulu names often referring to a person’s character or situation. It is also common for Zulu people to use proverbs and idiomatic expressions when they speak, as a way to express their feelings and emotions in a more sophisticated manner.
Overall, the Zulu language has had a profound influence on the culture and customs of the Zulu people. From its influence on storytelling and music, to its influence on the traditional naming system and the use of proverbs and idioms, the Zulu language has been a major part of Zulu culture for centuries. It is one of the most widely spoken languages in South Africa, and its influence is evident in many aspects of Zulu life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Zulu language is spoken by the majority of South Africans and is one of the 11 official languages in the country. Zulu is mainly spoken in the provinces of KwaZulu-Natal, Gauteng, Mpumalanga, and Limpopo, although there are also speakers of Zulu in other parts of the country. Zulu is an important language in South Africa, both historically and in terms of culture and identity, and is used widely in various aspects of daily life.



