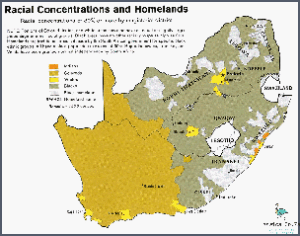
The majority of South Africans are of black African ancestry, and the country has a large population of mixed-race people. There are also significant numbers of people of European, Asian, and Arab descent.
The different ethnic groups in South Africa have a long history of conflict and tension. The apartheid regime of the 20th century was based on a system of racial segregation that favored the white minority at the expense of the black majority.
Since the end of apartheid in 1994, the different ethnic groups have been working to overcome their divisions and build a new, united South Africa.
Contents
What Are The Different Ethnic Groups In South Africa
South Africa is a diverse country with a variety of ethnic groups. The population is made up of approximately 79.5% Black African, 9.2% Colored, 8.9% White, and 2.5% Indian or Asian. The black population is made up of various ethnic groups, including the Nguni, Sotho, Shangaan-Tsonga, Venda, and Ndebele. The Colored population is a combination of African and European descent, with influences from the Khoisan, Dutch, and French. The White population is primarily of Dutch, German, and British descent. The Indian or Asian population is mainly of Indian and Pakistani descent. Each of these ethnic groups has unique cultural practices and traditions, making South Africa a truly multicultural nation.
Major Ethnic Groups in South Africa
South Africa is a culturally diverse country with many different ethnic groups. These ethnic groups consist of different backgrounds and each have their own unique history, culture and language.
The largest ethnic group in South Africa is the Black African group, which accounts for around 78% of the population. This group is composed of different ethnicities such as the Zulu, Xhosa, Tswana, Sotho, and Ndebele. These ethnicities have their own unique language and culture, and they have shaped much of South Africa’s history.
The Coloured population is the second largest ethnic group in South Africa, accounting for around 8.9% of the population. This ethnic group is made up of a mixture of different African, European, and Asian ancestries. They have their own unique culture and language, and they have a long history in South Africa.
The White population is the third largest ethnic group in South Africa, accounting for around 8.9% of the population. This ethnic group is made up of people of mostly European ancestry and they have a long history in South Africa, having been present since the 1600s.
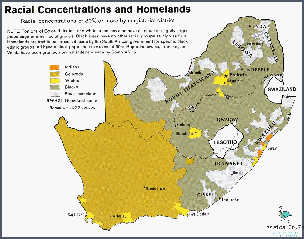
The Indian/Asian population is the fourth largest ethnic group in South Africa, accounting for around 2.5% of the population. This ethnic group is made up of people of Indian, Pakistani, and Chinese descent and they have been present in South Africa since the 1800s.
The San population is the fifth largest ethnic group in South Africa, accounting for around 0.3% of the population. This ethnic group is made up of people of the San ethnic group, who are the original inhabitants of South Africa. They have their own unique culture and language, and they have a long history in South Africa.
Overall, South Africa is made up of many different ethnic groups that each have their own unique culture and language. Each of these groups has contributed to the history and culture of South Africa and has made the country what it is today.
Minority Ethnic Groups in South Africa
South Africa has a rich and varied ethnic composition that is reflective of its turbulent history. The population of South Africa is comprised of a variety of ethnic groups, each with their own distinct cultural and linguistic heritage. From the Nguni, Sotho and Tswana people of the Bantu-speaking groups to the San, Khoi and Coloured groups of the Khoisan-speaking groups, South Africa is indeed a multi-ethnic nation.
The largest ethnic group in South Africa is the Zulu, who make up around 22% of the population. The Zulu people are a Bantu-speaking group who originated in present-day KwaZulu-Natal and are well known for their traditional stick fighting and textile weaving. Other Bantu-speaking groups include the Xhosa, Ndebele, Sotho, Shangaan, Venda and Tsonga people.
The second largest ethnic group in South Africa is the Afrikaner people, who are descended from Dutch settlers and make up around 16% of the population. Afrikaners are primarily concentrated in the Western Cape and Gauteng provinces, and they are well known for their traditional foods such as boerewors and bredie.
The Coloured group, who are descended from a mix of European, Malay and Khoisan ancestry, make up around 8% of the population. The Coloured population is concentrated mainly in the Western Cape, and they are well known for their unique cultural practices such as the Cape Malay cuisine and the Afrikaans language.
The San, Khoi and Tswana people, who are descended from the indigenous Khoisan-speaking groups, make up around 3% of the population. The San, Khoi and Tswana people are mainly concentrated in the Northern Cape and Limpopo provinces, and they are well known for their traditional healing practices and storytelling.
Although South Africa is a multi-ethnic nation, the majority of the population is still classified as “Black African”. This group makes up around 79% of the population and is made up of the various Bantu-speaking and Khoisan-speaking groups.

No matter their background, South Africans are united by their common language, English, and a shared passion for sports and music. As a result, South Africa is truly a diverse and vibrant nation that celebrates its many different ethnicities.
Influence of Ethnicity on South African Society
South Africa is a nation with a rich and diverse cultural heritage, and this is reflected in its multitude of ethnic groups. The most common ethnic groups in South Africa are African, White, Coloured, Indian or Asian, and Other.
The African ethnic group constitutes the majority of South Africa’s population, with around 80% of the population belonging to this group. This includes people of South African, Botswanan, Zimbabwean, Kenyan and other African descent. African culture is deeply rooted in the history and traditions of the country, with a strong emphasis on traditional values, language, and music.
The White ethnic group makes up around 8% of South Africa’s population, and is mainly comprised of Afrikaners, Dutch, and British descent. This group is largely associated with the colonial era and its effects on the country, and has traditionally held more political and economic power than other ethnic groups.
The Coloured ethnic group is made up of people of mixed ethnic backgrounds, including Khoisan, Malay, Indian and European descent. This group generally makes up around 8% of South Africa’s population, and has its own unique cultural identity.
The Indian or Asian ethnic group is made up of people of Indian, Pakistani, and Chinese descent, and makes up around 2% of South Africa’s population. This group is associated with the 19th century Indian indentured labourers and traders who settled in South Africa.
The Other ethnic group includes people of other ethnic backgrounds, including those from the Middle East and Latin America, and makes up around 2% of South Africa’s population.
Each of these ethnic groups has had an influence on South African society, and the country’s history, culture, and politics have been shaped by the various ethnic and cultural influences. From the impact of colonialism, to the effects of apartheid, to the rise of modern multiculturalism, South African society has been shaped and influenced by the various ethnic groups that call it home.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are a variety of different ethnic groups present in South Africa. These include the Black African population, which makes up 79.2% of the population, the White population (9.1%), the Colored population (8.9%), the Indian/Asian population (2.5%), and smaller populations of San, Khoisan, and other African ethnic groups. Each of these groups has their own unique histories, cultures, and languages, which contribute to the diverse and vibrant culture of South Africa.