The official languages of South Africa are Afrikaans, English, Ndebele, Xhosa, Zulu, Sesotho, Swati, Tswana, and Venda. These languages are the official languages of the country and are used in government, education, and the media. The languages were designated as official in 1994 and have been developing since that time.
Contents
What Are The 12 Official Languages Of South Africa
South Africa is a multi-cultural country with 11 official languages. These languages are Afrikaans, English, Ndebele, Northern Sotho, Sotho, Swazi, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa and Zulu. The 12th official language of South Africa is the South African Sign Language. This language was added as an official language in South Africa in May of 2003 and is used by deaf people all over the country. It is a rich language that uses hand signals, facial expressions and body language to communicate. All of the official languages of South Africa are recognized by the government and are used in government departments, courts, and other public service functions.
Overview of the 12 official languages of South Africa
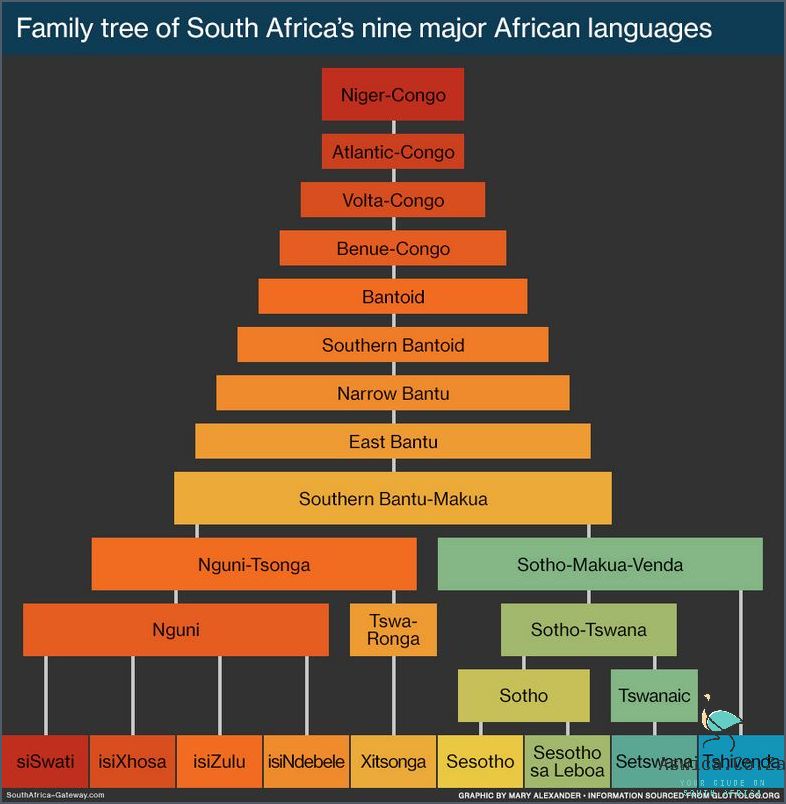
South Africa is a country rich in diversity and culture, and this is reflected in its twelve official languages. These languages, which include Afrikaans, English, isiNdebele, isiXhosa, isiZulu, Sepedi, Sesotho, Setswana, siSwati, Tshivenda, Xitsonga and Afrikaans, are all native to the country, and each has its own unique history and culture behind it.
Afrikaans is the most widely used language in South Africa, and is the mother tongue of nearly 8 million South Africans. It is a language derived from Dutch, and is spoken mostly in the Western Cape and Northern Cape regions. English is the other main language in South Africa, and is used widely in business, government, and education.
isiNdebele is spoken in the north of South Africa and is closely related to Zulu, Nguni and Xhosa. It is a language of the Nguni people, who have been living in South Africa for centuries. isiXhosa is the second most widely spoken language in South Africa and is the mother tongue of nearly 8 million South Africans. It is spoken mainly in the Eastern and Western Cape provinces, and is closely related to isiZulu.
isiZulu is the most widely spoken language of the Nguni people and is the mother tongue of nearly 10 million South Africans. It is spoken in the KwaZulu-Natal province, and is closely related to isiXhosa. Sepedi is the language of the Northern Sotho people, and is spoken in the North West, Limpopo and Free State provinces of South Africa.
Sesotho is the language of the Sotho people, and is the mother tongue of over 4 million South Africans. It is spoken in the Free State, Gauteng, Limpopo and North West provinces, and is closely related to Setswana. Setswana is the language of the Tswana people, and is spoken in the North West, Limpopo and Gauteng provinces.
SiSwati is a language of the Swazi people, and is spoken in the Mpumalanga, Limpopo and KwaZulu-Natal provinces. Tshivenda is the language of the Venda people, and is spoken in the Limpopo and North West provinces. Xitsonga is a language of the Tsonga people, and is spoken in the Limpopo and Mpumalanga provinces.
These twelve official languages of South Africa are a reflection of the country’s cultural diversity and form part of the unique South African identity. They are a reminder of the country’s history and the contribution of its many different communities to the nation.
History of each language
South Africa is a country of immense cultural and linguistic diversity. It is home to twelve official languages, all of which have fascinating histories that have shaped the nation as we know it today. From the early Khoisan languages thought to be spoken in South Africa over 20,000 years ago to the modern Romance and Bantu languages now spoken by millions of South Africans, each language has its own unique origin story. Here is a brief history of the twelve official languages of South Africa.
The first of these is Afrikaans, a language derived from Dutch. Afrikaans was first spoken among the Dutch settlers who arrived in South Africa in the 17th century. It was used mainly by the Dutch-speaking population of the Western Cape, and it was not until the 19th century that it began to spread to other parts of the country. Afrikaans was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1925.
The second official language of South Africa is English. English has been spoken in South Africa since the early 19th century when British settlers arrived in the Cape Colony. It was used mainly by the British-speaking population of the Cape, but it slowly spread to other parts of the country. English was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1926.
The third official language of South Africa is Ndebele, a Bantu language spoken mainly in the northern part of the country. Ndebele is believed to have originated in the early 19th century when the Ndebele people arrived in the area from the north. It was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1957.
The fourth official language of South Africa is Northern Sotho, a Bantu language spoken mainly in the northern part of the country. Northern Sotho is believed to have originated in the 17th century when the Sotho people arrived in the area from the north. It was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1957.
The fifth official language of South Africa is Sesotho, a Bantu language spoken mainly in the southern part of the country. Sesotho is believed to have originated in the 19th century when the Sotho people arrived in the area from the south. It was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1957.
The sixth official language of South Africa is Swazi, a Bantu language spoken mainly in the eastern part of the country. Swazi is believed to have originated in the 18th century when the Swazi people arrived in the area from the east. It was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1995.
The seventh official language of South Africa is Tsonga, a Bantu language spoken mainly in the southern part of the country. Tsonga is believed to have originated in the 18th century when the Tsonga people arrived in the area from the south. It was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1995.
The eighth official language of South Africa is Tswana, a Bantu language spoken mainly in the western part of the country. Tswana is believed to have originated in the 19th century when the Tswana people arrived in the area from the west. It was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1995.
The ninth official language of South Africa is Venda, a Bantu language spoken mainly in the northern part of the country. Venda is believed to have originated in the 18th century when the Venda people arrived in the area from the north. It was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1995.

The tenth official language of South Africa is Xhosa, a Bantu language spoken mainly in the eastern part of the country. Xhosa is believed to have originated in the 18th century when the Xhosa people arrived in the area from the east. It was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1997.
The eleventh official language of South Africa is Zulu, a Bantu language spoken mainly in the eastern part of the country. Zulu is believed to have originated in the 18th century when the Zulu people arrived in the area from the east. It was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1997.
The twelfth and final official language of South Africa is South African Sign Language, a language used mainly by the deaf population of the country. South African Sign Language is believed to have originated in the late 19th century when members of the deaf community began to use sign language as a means of communication. It was officially recognized as one of the official languages of South Africa in 1996.
Each of the twelve official languages of South Africa has its own unique history, and each has played an important role in the formation of the nation as we know it today. From Afrikaans to South African Sign Language, the history of each language is part of the larger story of South Africa’s cultural and linguistic diversity.
Impact of each language on South African culture
South Africa is home to a diverse cultural landscape, and with 12 official languages, it comes as no surprise that each language has had an impact on South African culture. From the unique clicks of Xhosa to the poetic tones of Afrikaans, each language has contributed to the rich heritage of South African culture.
The official languages of South Africa are Afrikaans, English, Ndebele, Northern Sotho, Sotho, Swati, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa and Zulu. Each language is spoken by around 3–4 million people, with the exception of Afrikaans, which is spoken by around 15 million people.
The language most widely spoken in South Africa is Zulu, followed by Xhosa. This can be attributed to the fact that these languages are the two most commonly spoken Bantu languages in South Africa. Zulu is a tonal language, meaning the same word can have different meanings depending on the tone it is spoken in. This has added a unique layer of richness to South African culture.
The language of Afrikaans has had a significant impact on South African culture too. It has its roots in Dutch and has since evolved to become its own unique language. Afrikaans has a literary history that goes back centuries, and it is considered to be one of the most poetic languages in the world. Afrikaans is also the language of the ruling party in South Africa, the African National Congress.
The other 10 official languages of South Africa have also had their fair share of influence on South African culture. These languages are all part of the Bantu language family and are spoken by various ethnic groups across the country. These languages have been used to express traditional customs and beliefs, and are still used for these purposes today.
Overall, the 12 official languages of South Africa have had a tremendous impact on South African culture. From the tonal sounds of Zulu to the poetic rhythms of Afrikaans, each language has added its own unique flavour to South African culture.
Conclusion
South Africa has 12 official languages: Afrikaans, English, Ndebele, Northern Sotho, Sotho, Swati, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa, Zulu and Southern Ndebele. These language groups are all represented in parliament and in the media. English is the most widely spoken language in South Africa, followed by Zulu.