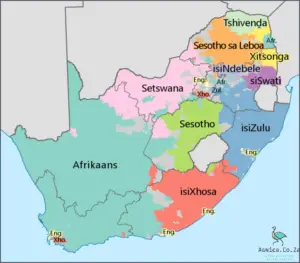
South Africa is a diverse country with an array of different cultures and languages. According to the 2011 census, there are 11 official languages spoken in South Africa; these are Afrikaans, English, Ndebele, Northern Sotho, Sotho, Swati, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa and Zulu. English is the most widely spoken language and is used as the language of instruction in most schools. Afrikaans is the second most commonly spoken language, and is derived from the Dutch language. It is spoken mainly in the western and northern parts of the country. The other nine languages are native African languages and are spoken predominantly in their respective regions.
Contents
What Language Is Spoken In South Africa
South Africa, the southernmost country on the African continent, is home to many diverse languages. The primary language spoken in South Africa is Afrikaans, a West Germanic language derived from Dutch. English is also widely spoken, as it is the official language of business and government. Other languages spoken in South Africa include Ndebele, Pedi, Sotho, Swazi, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa, and Zulu. All of these languages are part of the Bantu language family, which is the most widely spoken language family in Africa. While South Africa is known for its diversity, it is also known for its linguistic diversity.
Different languages spoken in South Africa
South Africa is a country of incredible diversity, with 11 official languages and many more regional dialects. From Afrikaans to Zulu, South Africa’s linguistic landscape is as varied as its cultural heritage. Here’s an overview of the main languages spoken in South Africa.
The most widely spoken language in South Africa is IsiZulu, spoken by around 24% of the population. It is a tonal language, which means that the same word can have different meanings depending on the tone in which it is pronounced. IsiZulu is the most common language used in KwaZulu-Natal and is also spoken in parts of the Eastern Cape, Gauteng, and Mpumalanga provinces.
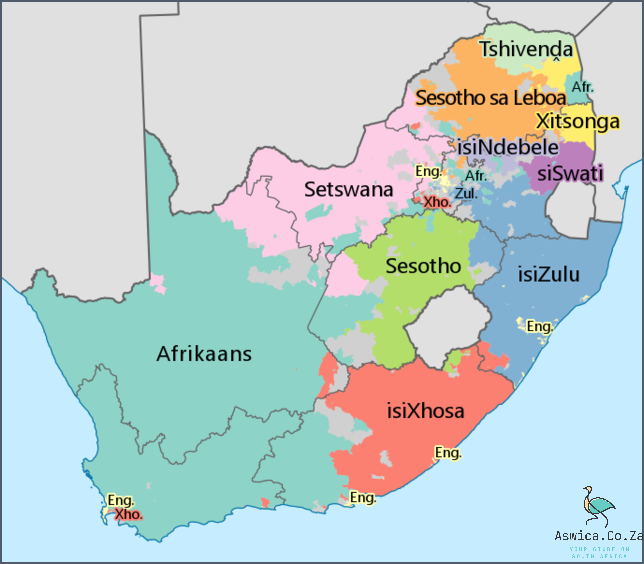
Afrikaans is a language that has its roots in Dutch, and is spoken by around 16% of South Africans. It is the most widely spoken language in the Western Cape and is also used in parts of the Northern Cape, Gauteng, and North West provinces.
English is the third most commonly spoken language in South Africa, with around 9% of South Africans speaking it as their main language. It is the language of government, business, and education, and it is spoken in all nine provinces.
South Africa’s other official languages include Northern Sotho, Sesotho, Tsonga, Swati, Tswana, Venda, Ndebele, and Xhosa. These languages are spoken primarily in the respective provinces where they originated.
In addition to the official languages, there are a number of other languages spoken in South Africa. These include other Bantu languages, such as Siswati, Swahili, and Fanagalo; European languages, such as Portuguese and German; and Asian languages, such as Gujarati and Hindi.
South Africa is a country of remarkable cultural and linguistic diversity. While the official languages are IsiZulu, Afrikaans, and English, there are many other languages spoken in this vibrant and diverse country.
Language policies in South Africa
South Africa has a unique linguistic landscape, with 11 official languages that represent its many ethnic and cultural groups. It is the only African nation to have such a diverse selection of languages and this diversity has been enshrined in South Africa’s language policies.
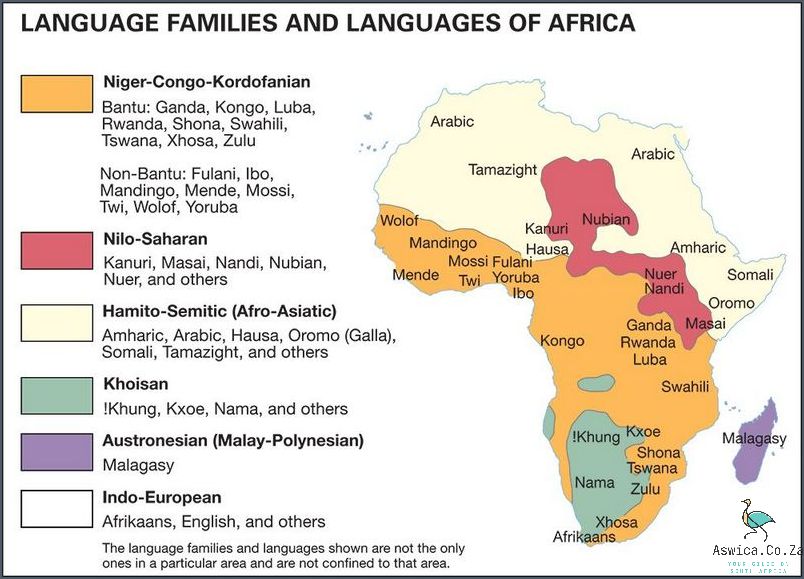
The official languages of South Africa are Afrikaans, English, Ndebele, Northern Sotho, Sotho, Swazi, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa, and Zulu. These languages were made official in the Constitution of the Republic of South Africa of 1996, which aimed to protect the linguistic and cultural rights of the country’s different ethnic and language groups.
The South African Constitution also states that the country should strive to promote the unity and development of the nation by “recognising the historically diminished use and status of the indigenous languages of South Africa”. To this end, the government has implemented various language policies to ensure that all of its citizens have access to education and services in their mother tongue.
The language policy of the South African government is to promote multilingualism in education, public service, and the media. This policy recognizes the right of all South Africans to use their mother tongue in education, public service, and the media, and encourages citizens to learn more than one language.
The South African government also has language-planning strategies in place to promote the development of the official languages. These strategies focus on the teaching and use of the official languages in schools, universities, and the media.
South Africa’s language policies have been successful in promoting language equality and helping the country’s many ethnic and language groups to co-exist. Despite this, there is still much work to be done to ensure that all South Africans have access to education and services in their mother tongue. This is an ongoing effort that will require continued commitment from the South African government and its citizens.
Impact of language on South African culture
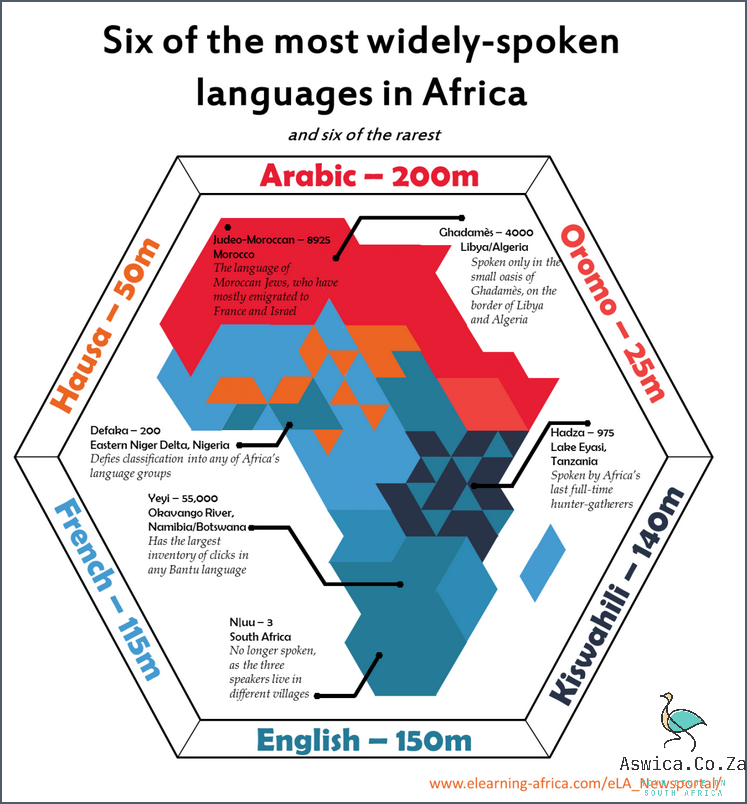
South Africa is a culturally and linguistically diverse nation, boasting 11 official languages and many more unofficial languages. Language has a powerful impact on South African culture. From the way people communicate and interact with each other to the way they express their identity and values, language is a fundamental part of South African culture.
The 11 official languages in South Africa are Afrikaans, English, Ndebele, Northern Sotho, Sotho, Swazi, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa and Zulu. Each language has its own unique history, with many of them having their roots in the country’s colonial past. Afrikaans, which is derived from Dutch, is the most widely spoken language in the country, followed by English.
Language has been a source of division in South Africa since the colonial era. Various languages have been used to oppress and marginalize minority groups. However, language has also been a powerful tool for uniting people and fostering a sense of community. Language is used to communicate values and celebrate cultural heritage. It has the power to bring people together and bridge cultural divides.
The impact of language on South African culture is evident in the way it is used to express identity. The term “ubuntu”, which roughly translates to “I am what I am because of who we all are”, is a popular term in South Africa. It is used to express the concept of unity and solidarity. Other words and phrases, such as “Sawubona” (“I see you”) and “Siyabonga” (“thank you”), are widely used to express respect and kindness.
Language is also an important part of South African literature. Many writers, such as Alan Paton and Nadine Gordimer, have explored the cultural nuances of the various languages spoken in South Africa. These authors have provided rich insight into the complexities of the South African experience.
In conclusion, language has a significant impact on South African culture. It is a powerful tool for expressing identity, values, and cultural heritage. It has the power to unite people and foster a sense of community. Language is an integral part of South African literature and culture.
Conclusion
In South Africa, a variety of languages are spoken. The most common languages spoken in South Africa are English and Afrikaans. Other languages spoken in South Africa include Zulu, Xhosa, and Swazi.




