The Bantu people are an ethnic group that is native to Africa. The term "Bantu" means "people" or "humans" in the Bantu language. The Bantu people are the largest ethnic group in Africa, and they are also one of the largest ethnic groups in the world. The Bantu people are thought to have originated in West Africa, and they began to migrate to other parts of Africa around 2,000 years ago. The Bantu migration is thought to have been triggered by a number of factors, including drought, overpopulation, and political conflict. The Bantu migration resulted in the spread of the Bantu language and culture to other parts of Africa. The Bantu people eventually settled in all of the countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
The Bantu people began to migrate to South Africa around 1,000 years ago. The Bantu migration to South Africa was gradual, and the Bantu people slowly began to settle in various parts of the country. The Bantu people were attracted to South Africa because of its mild climate and its abundance of natural resources. The Bantu people slowly began to displace the indigenous people who were living
Contents
When Did The Bantu Arrive In South Africa
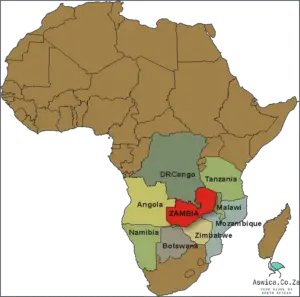
The Bantu arrived in South Africa between the 1st and 5th centuries AD. They came from the north, which is now modern day Nigeria, Cameroon, and Congo. This migration of people was known as the Bantu Expansion. The Bantu brought with them their culture, language, and advanced farming techniques. As they moved south, they interacted with the local inhabitants and established trade routes. Eventually, they settled in the southern parts of South Africa and the Central African Republic. The Bantu have had a significant impact on South African culture, with their language and customs still being used today.
Migration of Bantu people and the Bantu Expansion
The Bantu people are an ethnic group that originated in West Africa and spread to many different parts of the continent over the centuries. The Bantu Expansion, as it is often referred to, began around 2000 BCE and lasted until the early 19th century. This migration of the Bantu people was a result of various factors such as population growth, agricultural advancements, and the search for new resources.
The Bantu Expansion began in the Cameroon-Nigeria border area and moved in a southwesterly direction. As they moved, they spread their culture, language, and agricultural knowledge. With the invention of the iron axe, the Bantu people were able to clear more land for farming which allowed them to expand even further. By 1000 CE, the Bantu had reached the Great Lakes region of Central Africa.
By the 16th century, the Bantu had reached the southern tip of Africa. This was the furthest extent of the Bantu migration. As they moved south, they encountered the Khoisan people who were hunter-gatherers. The Bantu and Khoisan people interacted and exchanged ideas, which helped them both to become more advanced and successful.
The arrival of the Bantu people in South Africa had a significant impact on the region. They brought with them their culture and language, which was adopted by many of the native peoples in the area. Additionally, their agricultural methods allowed them to produce more food than before which helped to increase the population of the region.
The Bantu Expansion was one of the most significant migrations in human history. It allowed the Bantu people to spread their culture, language, and agricultural knowledge to many different parts of the continent. It also created a diverse and multicultural society in South Africa that exists to this day.
When did the Bantu arrive in South Africa
The arrival of the Bantu in South Africa is a fascinating part of the country’s history. This group of people, also known as the Bantu-speaking peoples, were amongst the first to arrive in the region and their arrival has had a profound impact on the culture and history of the region.

The Bantu migration is believed to have begun around 2000 BC, when small groups of Bantu-speaking people began to move southwards from modern-day Cameroon and Nigeria. This migration was spurred on by the need for more arable land, as well as for an escape from the political turmoil in their native lands.
The Bantu migration was slow and steady, and it is believed that they arrived in South Africa around 1000 AD. They settled in the northern parts of the country and slowly spread out, eventually reaching the Cape by 1700 AD.
The Bantu brought with them a wealth of knowledge and skills, including agriculture and metalworking. They also brought their own language, Bantu, which is still spoken in many parts of the country today.
The impact of the Bantu on South Africa was immense. They brought with them a new way of life, and their influence can still be seen in the cultures and languages of the region. In addition, the Bantu’s arrival had a profound effect on the political landscape of the country, as they quickly rose to be a powerful force in the region.
The Bantu’s arrival in South Africa was a major turning point in the history of the country, and their influence can still be felt today. From their language to their cultural and political contributions, the Bantu have left a lasting legacy in South Africa.
Impact of the Bantu migration on the African continent
The Bantu migration is one of the most significant events in African history. It was a major population movement that shaped the culture of much of Sub-Saharan Africa. Beginning around 2000 BC, the Bantu people began migrating south and east from their homeland in West Africa. The Bantu migration had a major impact on the African continent, bringing new cultures, languages, and skills to many areas of Sub-Saharan Africa.
The Bantu migration began in the West African rainforests, in an area known as the Niger-Congo region. This region was the home of several ancient African cultures, including the Bantu. Over time, these cultures adapted to the environment and developed their own unique language, culture, and technology. As the environment changed, the Bantu people began to move south and east in search of new resources and land.
The Bantu migration eventually reached South Africa around 1000 BC. This was a significant event in African history, as the Bantu brought with them their unique language, culture, and technology. This new culture had a profound impact on the region, introducing new crops, tools, and techniques. The Bantu also brought with them their social and political structures, which laid the foundations for the development of the various African kingdoms that later flourished in the region.
The Bantu migration also had a profound effect on the languages of the region. As the Bantu spread, their language spread with them, and over time it became the most widely spoken language in Sub-Saharan Africa. This language was later known as Bantu, and it is still spoken in many parts of Africa today.
The Bantu migration had a lasting impact on the African continent. It brought new cultures, languages, and technologies to many parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. It also laid the foundations for the development of many African kingdoms, and its language is still spoken in many parts of the region. The impact of the Bantu migration is still felt today, and it serves as a reminder of the importance of population movements in shaping the history of the African continent.
Conclusion
The Bantu arrived in South Africa between 1,500 and 2,000 years ago. The exact date is not known, but it is thought that they came from the west, across the Congo River. They brought with them their own language and culture, which eventually spread across the country. Today, the Bantu make up the majority of the population of South Africa.