Poverty is a major issue in South Africa and has been for many years. It is estimated that around 40% of the population is living in poverty, with the majority of those affected being black South Africans. Poverty has been linked to a variety of issues in South Africa, including high unemployment, inequality, and poor education. It has also been linked to crime, health problems, and social exclusion.
Poverty affects many aspects of life in South Africa. It limits the access to basic amenities and health services, and limits educational opportunities. Poor households in South Africa are often unable to afford basic necessities, such as food, clothing, and housing. This leads to a cycle of poverty, as it makes it difficult to break out of the cycle.
Poverty also has a large impact on the economy of South Africa. It affects the country’s economic growth, as most of the country’s population is unable to participate in the economic activities that could help to drive the economy. This means that there is less money available for investment and growth, which affects the overall development of the country.
In order to combat poverty in South Africa, the government has implemented a variety of initiatives, including the National Development Plan
Contents
What Role Does Poverty Play In South Africa
Poverty is a major issue in South Africa, with around half of the population living below the poverty line. It has impacted many aspects of life in South Africa, especially in more rural areas. Low levels of education and lack of access to basic services such as healthcare, sanitation, and safe drinking water further contribute to poverty levels in the country. Poverty in South Africa is also associated with race, as the majority of people in poverty are black. This racial inequality has been a long-standing issue in South Africa and still has an impact on poverty levels today. Poverty in South Africa has been linked to a range of other issues such as crime, violence, and poor health. In order to address the issue of poverty in South Africa, the government needs to implement policy changes that will help to create jobs and provide access to essential services.
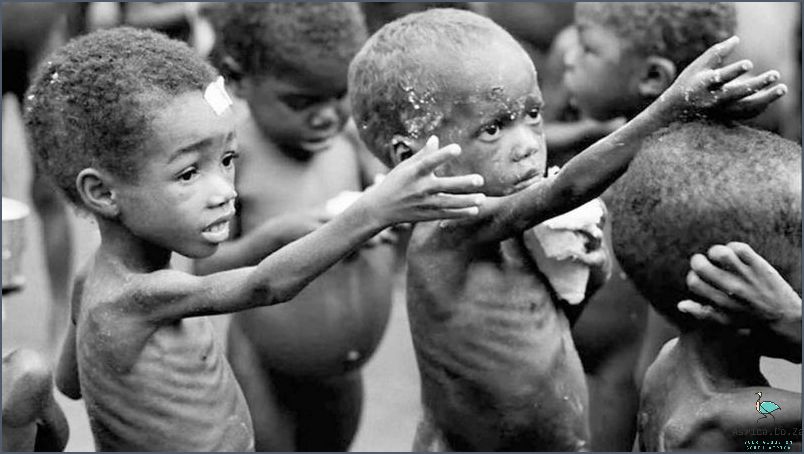
History of poverty in South Africa
The history of poverty in South Africa is both a long and complex one. Despite being one of the most affluent countries in the world, South Africa has long grappled with the issue of poverty.
The roots of poverty in South Africa trace all the way back to colonial times, when the British Empire and other European powers claimed sovereignty over much of Africa. This created a system of racial segregation and oppression that denied many South Africans the opportunity to rise out of poverty. To this day, there is a stark racial divide between the wealthy and the poor in South Africa, with the majority of the population living in poverty being black, colored, and Indian.
The apartheid era, which lasted from 1948 until 1994, further entrenched poverty in South Africa. The system of racial segregation that was implemented during apartheid denied many South Africans access to education, employment opportunities, and other basic services, which kept them in a cycle of poverty.
In the post-apartheid era, South Africa has made significant strides towards alleviating poverty. Various programs and initiatives have been implemented to help the poor, such as the provision of grants and subsidies for housing, education, and healthcare. In addition, the government has increased its focus on job creation and economic development, which has helped to create more opportunities for South Africans to escape poverty.
Despite these efforts, poverty remains a major issue in South Africa. Chronic poverty and inequality persist, as well as high levels of unemployment and a lack of access to basic services. As such, it is clear that the issue of poverty in South Africa is a complex one, and one that will require a concerted effort from all levels of society if it is to be successfully addressed.
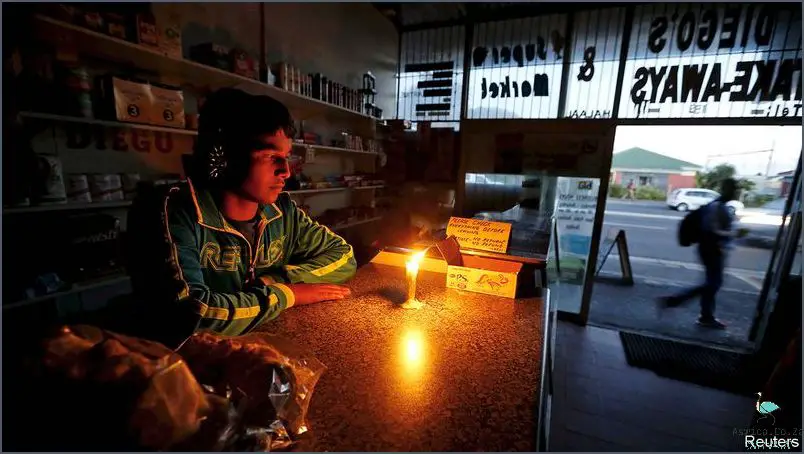

Causes of poverty in South Africa
Poverty is an endemic issue that has plagued South Africa since its inception. It is one of the most pressing issues facing the nation today, with more than half of the population living below the poverty line. The causes of poverty in South Africa are complex and multifaceted, and include structural issues such as economic inequality, an inequitable distribution of resources, and a lack of access to basic services.
The legacy of Apartheid still plays a major role in South Africa’s poverty level. Under Apartheid, the government pursued a policy of racial segregation, with white citizens enjoying a much higher standard of living than those of color. This included access to education, health care, and employment opportunities, which often resulted in higher wages and a better quality of life. The end of Apartheid in 1994 did not bring with it an instant end to poverty; instead, the economic inequality that had been created by the system remained largely intact. This has resulted in a situation in which the majority of South Africa’s citizens remain in poverty, with access to basic services still severely limited.
In addition to the legacy of Apartheid, there are other structural issues that contribute to the high levels of poverty in South Africa. These include a lack of economic diversification, an over-reliance on extractive industries, and the lack of access to capital. This has resulted in a situation in which many South Africans are unable to find employment, and those that do find employment often earn low wages due to the lack of opportunity. Furthermore, rising inflation and the cost of living have made it difficult for many to make ends meet, leading to a situation in which many are unable to afford basic necessities.
The role of poverty in South Africa cannot be overstated; it is a complex and pervasive issue that has far-reaching consequences. In order to address the issue, it is essential to take a holistic approach that takes into account the structural issues that are at the root of the problem. This includes addressing the legacy of Apartheid, promoting economic diversification, improving access to capital, and providing access to basic services such as education, health care, and employment opportunities. Only by addressing the root causes of poverty in South Africa can the nation hope to achieve a more equitable and prosperous future.
Impact of poverty on South African society

Poverty has been a long-standing issue in South African society that has been increasingly difficult to resolve. While there is no single cause of poverty, it is a pervasive problem that is affecting a large portion of the population. In order to tackle poverty in South Africa, it is important to understand the various factors that contribute to it and the impact that it has on society.
At its core, poverty is the lack of sufficient resources to meet the basic needs of life – such as food, shelter, clothing, education and healthcare. This lack of resources can be caused by a number of factors, including inequality, unemployment and marginalization. As such, poverty can be viewed as both a cause and an effect of a range of social and economic issues.
In South Africa, poverty is particularly widespread and deeply entrenched. According to the World Bank, the poverty rate in South Africa stands at 55.5% – one of the highest in the world. This has serious implications for the population, as it means that millions of people are living in extreme poverty, lacking access to basic needs and services.
The consequences of poverty on South African society are far-reaching. It has a direct impact on the quality of life for those living in poverty, as well as for the wider population. Poverty affects access to education, healthcare and other essential services, reducing social mobility and trapping people in a cycle of deprivation. It also increases inequality, as those in poverty are often disproportionately affected by the lack of resources and opportunities that are available to them.
Furthermore, poverty has a significant economic impact on South African society. It reduces economic growth and increases the burden on public services, as resources are drained away to support those living in poverty. This can result in an economic downturn, as well as a negative impact on government spending.
Ultimately, the impact of poverty on South African society is clear. It is essential that measures are taken to address the root causes of poverty, so that the population can be provided with the resources and opportunities it needs to break the cycle of deprivation and achieve long-term economic growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, poverty plays a major role in South Africa. Despite economic growth and development, poverty has remained high in South Africa and has become more entrenched over the years. Poverty has been linked to a number of issues such as lack of access to education, employment opportunities, healthcare and basic services. The effects of poverty are particularly felt in rural and informal settlements, where access to basic services is limited. Poverty has also been linked to crime and violence, as well as to HIV/AIDS. In order to address these issues, the South African government has implemented several initiatives to tackle the root causes of poverty and to reduce poverty levels. However, more needs to be done to ensure that all South Africans have access to basic services, education, health care and employment opportunities.