Africa GDP Map is an interactive map that shows the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of African countries. It is used to compare the GDP of countries in Africa and to identify trends in economic growth across the continent. The map is based on data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World Bank. It gives an overview of the relative size of the economies of African countries and the progress they are making in terms of economic growth. It also shows the distribution of GDP across the continent and the countries with the highest and lowest GDP per capita. The map is a useful tool for governments and businesses to understand the economic dynamics of the continent and to make more informed decisions.
Contents
Africa Gdp Map
The Africa GDP Map is an interactive map that shows the Gross Domestic Product of the countries in Africa. It provides a visual representation of the continent’s economic performance, allowing viewers to quickly identify countries with the highest and lowest GDP. The map is organized by region, and displays the GDP for each country in US dollars. It also includes a breakdown of the GDP by sector, such as industry, services, and agriculture. The map is a valuable tool in understanding the economic development of Africa and offers key insights into the continent’s economic prospects. It is also a great resource for investors looking to identify opportunities in the region.
Discuss Africa’s GDP, its growth in recent years and its impact on the continent
Africa is the second largest continent in the world, and has some of the most diverse and vibrant economies in the world. Despite its immense natural resources, the continent’s GDP has historically lagged behind the majority of the world. Over the past two decades, however, the continent has seen tremendous economic growth, with Africa’s GDP rising from $1.2 trillion in 2000 to almost $3 trillion in 2020.
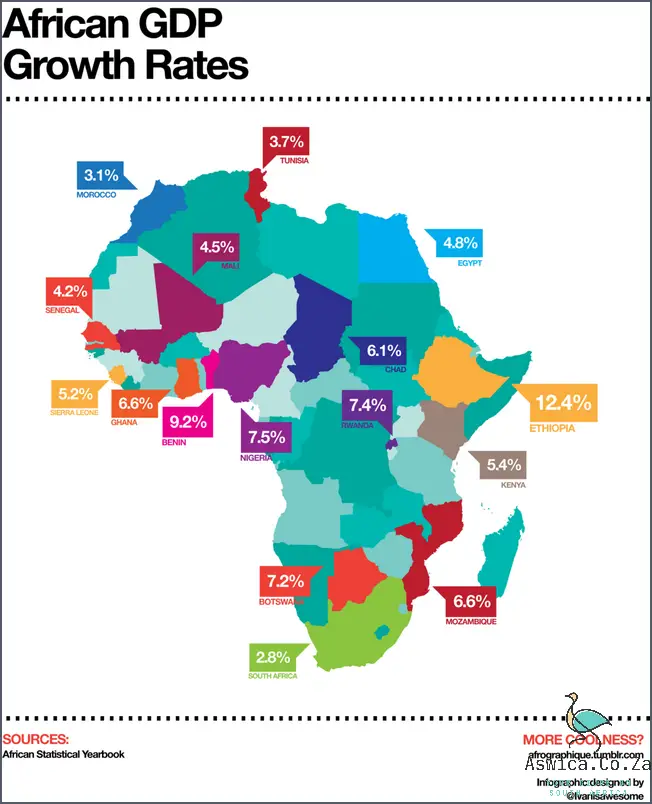
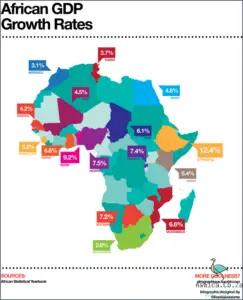
This economic growth has been largely driven by increased investment from foreign powers, as well as a burgeoning local business environment. Africa has seen a huge influx of foreign investment from both public and private sources, with the continent now being home to some of the world’s largest multinational corporations. This has allowed Africa to capitalize on its vast natural resources and its large population.
At the same time, Africa has seen an increase in the number of startups and small businesses, which have helped to diversify the continent’s economy. This has allowed Africa to diversify its sources of income, creating jobs and providing economic opportunities for many people. Additionally, many African countries have adopted policies that encourage economic growth, such as eliminating tariffs and subsidies, which have helped to stimulate the growth of the African economy.
The rise in Africa’s GDP has had a positive effect on the continent, allowing for improved living standards and an enhanced level of access to healthcare and education. In addition, the continent has seen a decrease in poverty, with the number of people living in absolute poverty dropping from over 50% in 1990 to less than 40% in 2020. This has been made possible due to the increased economic opportunities that have been created by the continent’s increased economic growth.
Overall, Africa’s GDP has had a significant impact on the continent, allowing for increased economic opportunities and improved living standards. The continent’s growth has been largely driven by foreign investment, local business development, and the adoption of policies that promote economic development. As Africa continues to grow, it will be important to ensure that the continent is able to capitalize on its natural resources and its large population in order to create a more prosperous future for all of its citizens.
Explore the various methods of mapping Africa’s GDP, such as by country, region, or by sector
Mapping Africa’s GDP is a complex yet essential task for economists and policy makers alike. Understanding the economic performance of one of the world’s most diverse regions can provide valuable insight into the global economy. There are various methods of mapping Africa’s GDP, such as by country, by region, or by sector.
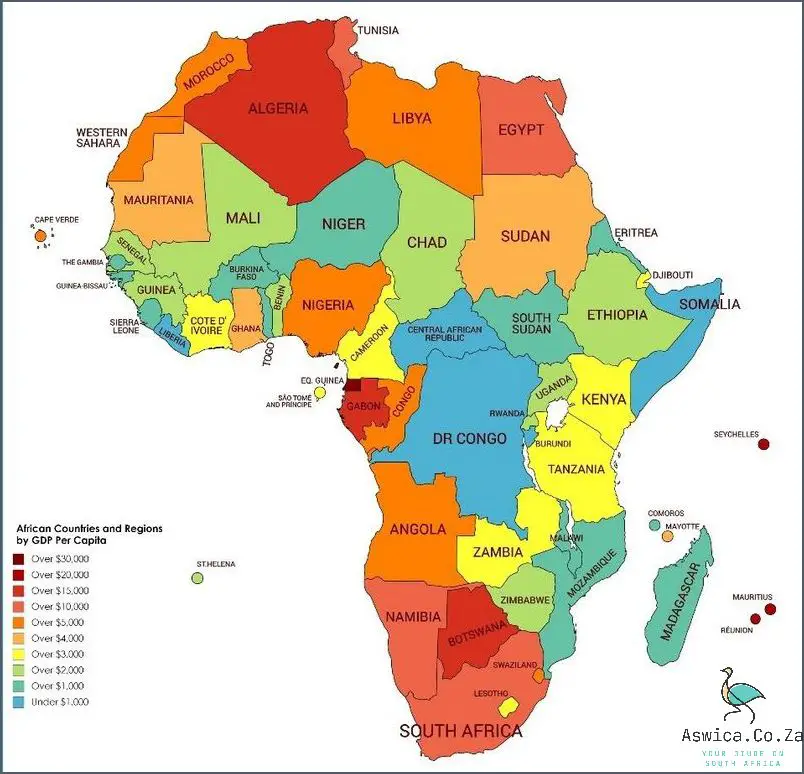
Mapping Africa’s GDP by country is a useful tool for identifying the relative economic performance of each nation, as well as the overall GDP of the region. This method of mapping provides an insight into the economic progress of each nation and the challenges it faces, as well as its potential for growth. For example, a country-by-country map of Africa’s GDP would reveal that the continent’s largest economy is that of South Africa, while the smallest is that of Gambia.
Mapping Africa’s GDP by region is also a useful tool for assessing the economic performance of a particular region. This method of mapping can be especially useful for identifying the economic disparities between countries in the same region. For example, a regional GDP map of Africa would reveal that GDP per capita in North Africa is significantly higher than in sub-Saharan Africa.
Finally, mapping Africa’s GDP by sector is a useful tool for understanding the economic activities that are driving the continent’s growth. This method of mapping can be used to identify the sectors that are contributing the most to the continent’s economic development, as well as those that are lagging behind. For example, a sector-by-sector map of Africa’s GDP would reveal that the continent’s most important sectors are agriculture, manufacturing, and services.
Mapping Africa’s GDP is an essential task for understanding the continent’s economic performance. By using the various methods of mapping, such as by country, region, or sector, economists and policy makers can gain valuable insights into the economic challenges and opportunities that the continent faces.
Examine the advantages and disadvantages of each method of mapping GDP
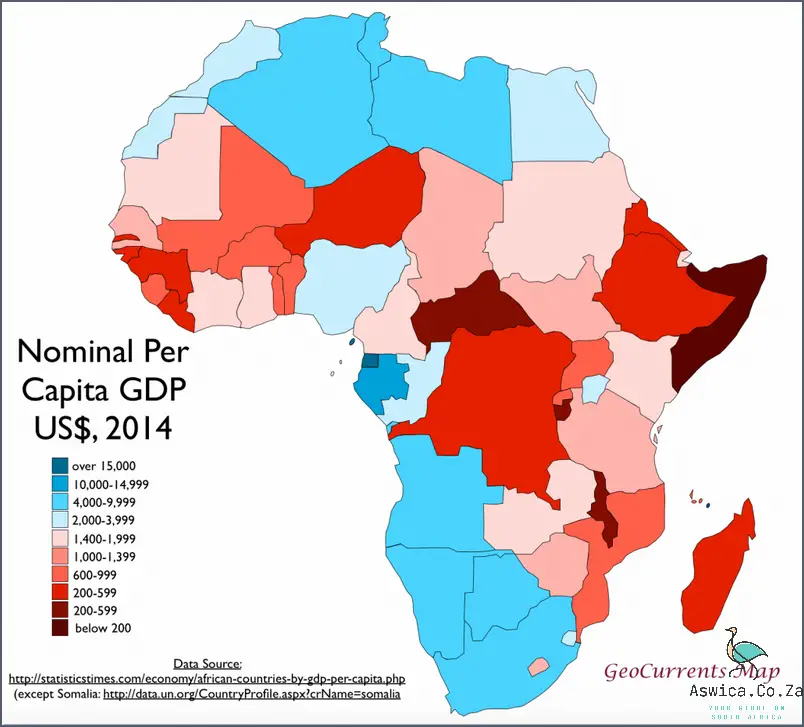
Mapping GDP is an important tool for understanding economic growth and progress. It can provide a visual representation of a country’s growth over time, or help identify areas of potential growth. Different methods of mapping GDP provide different advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to examine the pros and cons of each before making a decision.
One of the most common methods of mapping GDP is the cartographic method. This involves creating a geographic map showing the GDP of each region or country. The advantage of this method is that it provides a visual representation of the economic situation in each region. This can be useful for identifying areas of potential growth and areas that need to be addressed. The main disadvantage of this method is that it does not provide a detailed breakdown of the GDP data. It simply shows the overall picture, which can be difficult to interpret.
Another method of mapping GDP is the statistical method. This involves using statistical methods to identify trends and patterns in the data. This can be useful for understanding the underlying economic factors that are driving the growth. The main disadvantage of this method is that it can be time-consuming and complex to interpret the data.
Finally, the economic modeling method is used to create a model of the economy and the GDP of each country or region. This can provide a more detailed view of the economic situation in each area, but it can also be difficult to interpret. The advantage of this method is that it can provide a better understanding of the economic forces at work. The disadvantage is that it can be difficult to accurately model the economy, which can lead to inaccurate predictions.
Overall, there are a number of methods of mapping GDP and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. The best method will depend on the specific needs of the user, so it is important to consider all of the available options and choose the one that best suits the user’s needs.
Conclusion
The Africa GDP map is a useful tool to analyze the economic development of African countries. It provides a comprehensive overview of the continent’s GDP growth by country, and can help to identify areas where investment or aid may be needed. It has also highlighted the disparities between countries, with some countries having more than double the GDP of other countries. Overall, the map is a valuable resource for understanding the economic development of African countries and has the potential to inform policy decisions and development strategies.




