
The Bantu Education Act of 2009 is important to know because it seeks to address the shortage of quality education opportunities for black African students in South Africa. The Act sets out the government’s plan to provide free and compulsory education for all black African students up to the age of 18. The Act also establishes a fund to support the implementation of the plan.
Contents
Why Is The Bantu Education Act Important To Know
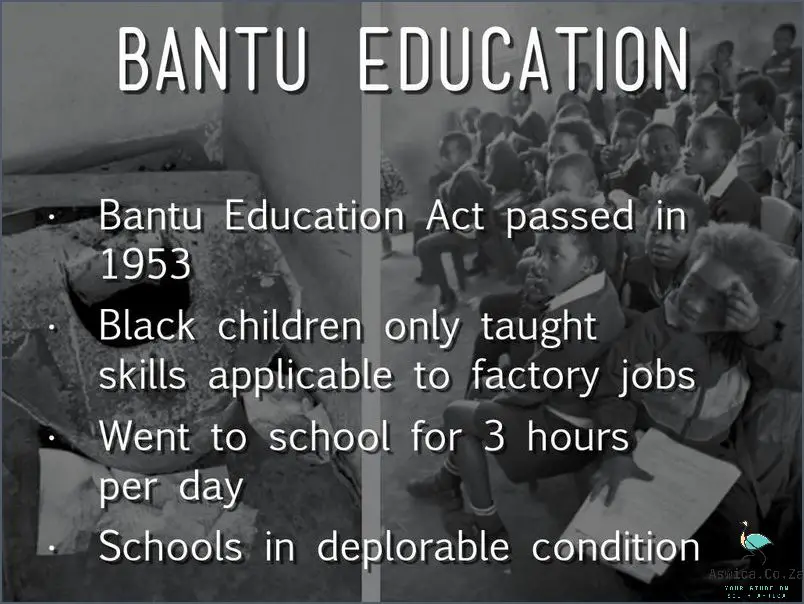
The Bantu Education Act of 1953 was an important step in South African history that has had lasting impacts. It segregated South Africa’s education system and created a system of different schools for different racial groups. This act was the first major step towards the implementation of Apartheid. It was designed to limit the educational opportunities of those classified as black or African in South Africa. It limited their access to higher education, reduced their educational standards, and made it more difficult for them to advance in their careers. The Bantu Education Act was a major factor in the long-term inequality between white and black South Africans. It is important to know the Bantu Education Act because it has had an enormous impact on South African society and its consequences are still felt today. It is important to understand the history of this act in order to understand the current situation in South Africa.
Background: Pre-Apartheid Education System in South Africa
The Bantu Education Act was a cornerstone of the Apartheid government’s policies in South Africa during the mid-20th century. The Act served to provide the government with an institutionalized form of racial segregation, which had been occurring in South Africa since the early 1900s. The Bantu Education Act was an attempt to create a distinct, separate educational system for black South Africans, one that would be distinct from the white South African education system.
Prior to the implementation of the Bantu Education Act, South African education had been predominantly segregated due to the racial divisions that were already in place. Black South Africans were largely excluded from the formal educational system, with most education taking place in mission schools or in informal settings. This lack of access to formal education, combined with the economic disadvantages faced by black South Africans, made it difficult for black South Africans to obtain the qualifications and skills necessary to pursue higher education or gain employment.
The Bantu Education Act aimed to address these issues by providing a distinct, separate system of education for black South Africans. The Act limited the curriculum of black schools to the basics of reading, writing, and arithmetic, while white students were able to pursue a variety of subject areas. The Act also limited the financial resources available to black schools, meaning that they were unable to access the same resources as white schools. This, in turn, led to a lower quality of education for black South African students.
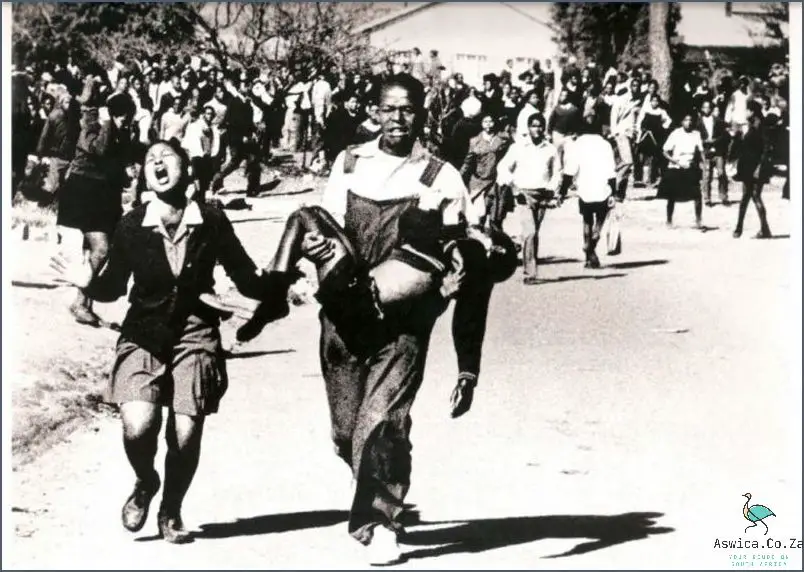

The Bantu Education Act was a major setback for black South Africans, and its legacy can still be seen today. Despite the end of Apartheid, the educational disparities between white and black South African students persist. The Act is also seen as having a significant role in the perpetuation of racial inequalities in South Africa, with many believing that it contributed to the creation of a system designed to keep black South Africans in a state of economic and political disadvantage.
For these reasons, it is important to understand the history of the Bantu Education Act and its impacts on South African education. Only by understanding this history can we begin to address the underlying issues causing educational disparities in South Africa and work towards creating an equitable and inclusive education system.
Impact of the Bantu Education Act on South African Education System
The Bantu Education Act of 1953 is an important part of South African history and is particularly relevant to the country’s educational system. It laid the foundation for the kind of education system that South Africans still experience today. This act was the result of a policy that the National Party, which had just come to power, had laid out to create a racially segregated educational system. The goal was to ensure that black South Africans were not given the same educational opportunities as white South Africans.
The effect of this Act was to create a separate and unequal educational system for black South Africans. It stripped black students of their autonomy and severely limited the educational opportunities available to them. This meant that black students were not able to access the same quality of education as white students, and were less likely to be able to pursue higher education.
The Bantu Education Act had a profound impact on the South African education system. This Act was used as the basis for discrimination and segregation in the educational system. This meant that black students were not given the same access to quality education as white students, and this in turn had a major impact on their ability to participate in and benefit from the South African educational system.
The Bantu Education Act was eventually repealed in 1979, but the legacy of this Act still lingers in the South African education system. There is still a large gap between the educational opportunities available to black and white students. In addition, many of the discriminatory practices that were in place during the time of the Bantu Education Act still exist today.
The Bantu Education Act is an important piece of South African history and its legacy is still felt today. It is important to remember that this Act had a huge impact on South African education system, and it is essential to continue to strive for educational equity and equality. By recognizing the impact of the Bantu Education Act and continuing to work towards equitable educational opportunities for all South Africans, we can ensure that the legacy of this Act is not forgotten.
Implications of the Bantu Education Act in Post-Apartheid South Africa
The Bantu Education Act was one of the most important pieces of legislation that was enacted in post-apartheid South Africa. It was enacted in 1953 under the apartheid government and was designed to separate and segregate racial groups within the education system. This act had far-reaching implications for South Africa’s post-apartheid society, including the economic and social opportunities that were available to black South Africans.
The Bantu Education Act was designed to ensure that black South Africans received an inferior education compared to white South Africans. Black students were taught in separate schools and given separate textbooks, which were of lower quality than those given to white students. Black students were also discouraged from taking advanced classes and were limited to vocational training. This meant that black South Africans were denied access to the same level of education and opportunities as white South Africans.
The implications of the Bantu Education Act were far-reaching. It had a significant impact on the economic opportunities available to black South Africans. Many black South Africans were unable to access the same quality of education that white South Africans had access to, which meant that they were unable to compete for the same jobs and positions in the workforce. This led to a large disparity in the wages and salaries of black and white South Africans, as well as a large gap in the wealth of the two groups.
The Bantu Education Act also had a major impact on the social opportunities available to black South Africans. Black South Africans were not allowed to participate in many of the social activities that white South Africans had access to, such as sports teams and extra-curricular activities. This had a major impact on the development of black South Africans, as they were unable to build relationships with their peers or participate in activities that could help them develop skills and experiences.
The Bantu Education Act has had a major impact on South African society in post-apartheid South Africa. It has had a profound effect on the economic and social opportunities available to black South Africans. The act has been a major contributing factor to the wealth and income gap between white and black South Africans, as well as the disparities in social opportunities that are available to black South Africans. The act has had a major impact on the development of black South Africans and their ability to access the same opportunities as white South Africans.
Conclusion
The Bantu Education Act was an important and controversial piece of legislation that was enacted in South Africa in 1953. The Act was designed to further the segregation of the black population from the white population, and to ensure that black children received an inferior education. The Act was widely criticized by opponents of Apartheid, and it was eventually repealed in 1976. Despite its controversial nature, the Bantu Education Act is an important part of South African history, and it is important to understand its impact on the country.



